Articles
Comparison of Isocratic and Gradient Elution
posted : 19 بهمن 1399
By : Kianshar D research team
There are two kinds of elution in HPLC technique :
1- Isocratic elution
2- Gradient elution
Isocratic elution refers to maintaining a constant concentration in the mobile phase whereas gradient elution refers to maintaining a varying concentration in the mobile phase. By the other words the isocratic and gradient elution describe the properties of the mobile phase.
What is Isocratic Elution?
Isocratic is a kind of elution in HPLC technique in which the mobile phase has a constant concentration during the chromatographic process. Isocratic elution is usually not the preferred method because of its two important disadvantages :
1- Flat and broad peaks
In isocratic elution the peak width of analyte is increased with the retention time linearly. However, this leads to a disadvantage , the late-eluting peaks for late elution get very flat and broad and become difficult to be recognized as peaks.
2- No peak selectivity by changing the column dimensions
In isocratic elution, the selectivity does not change according to the column dimensions. This means there is a limitation in making the HPLC separation more selective by the users when they decide to use the columns with different lengths and diameters.
What is Gradient Elution?
Gradient is a kind of elution in HPLC technique in which the mobile phase has a varying concentration during the chromatographic process. For example , a common separation method uses methanol 10% initially which ends at 90%, by increasing the concentration gradually. The gradient elution offers 2 important advantages :
1- Narrow and high peaks
Gradient elution consists of two components : a weak solvent which allows the solute to elute slowly and a strong solvent which causes the rapid elution of the solute. Water is an example of weak solvent and Methanol is an example of strong solvent in Reversed Phase HPLC. By using a complex of weak and strong solvents we can manage to decrease the retention time of later eluting analytes which leads to faster separation and acquiring much better peaks .
2- peak selectivity by changing the column dimensions
In gradient elution technique, the elution order changes with the changes in column lengths and diameters.
Figure 1 : the effect of isocratic and gradient elutions over the retention time and appearance of the peaks in chromatogram
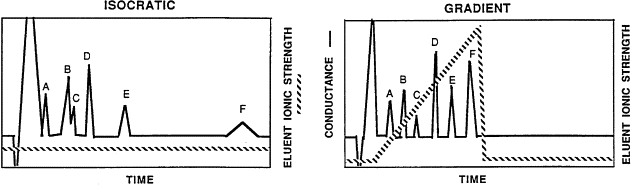
The below table shows the main differences in brief between isocratic and gradient elution.
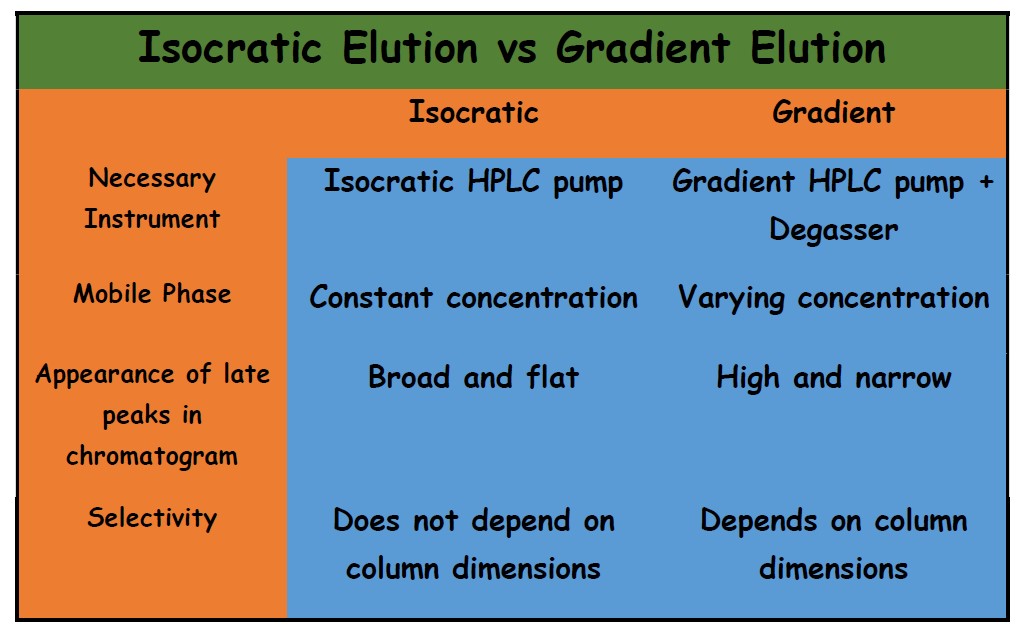
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reference:
1. “Gradient Elution.” Gradient Elution – an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics
2- https://b2n.ir/s53465